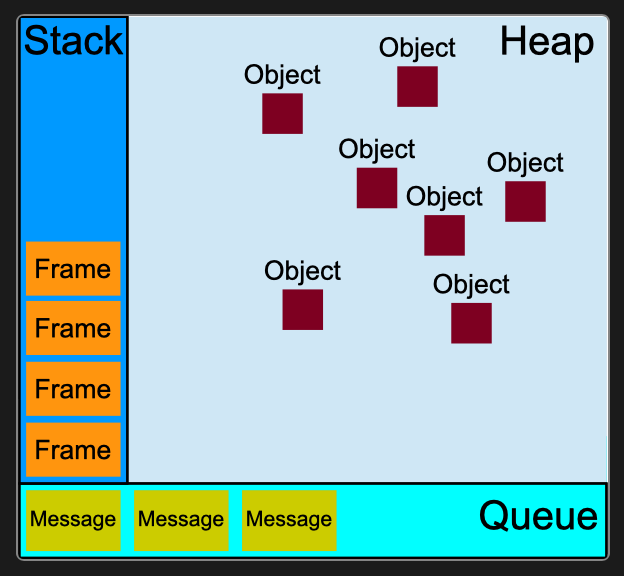
- 帧:执行原子单元?
- 栈:写作 Call Stack
- 堆:存储对象
- 在寄存器上存放基本类型数据&指针的,也叫栈!!⚠️注意区分
- 队列:写作 Call Queue
- FIFO
- 分为 microtasks queue (job queue)
- Promise
- process.nextTick(NodeJS)
Object.observe(废弃)- MutationObserver
- 和 macrotasks queue(callback queue)
- script
- timers:setTimeout/setInterval
- I/O events
- user interface events
TLDR;
#
javascript-event-loop-call-stack[1]Call stack#
- “单线程”| each function call is being added to the call stack and removed once it finishes.
- 压栈/出栈| the stack processes each function call is following the LIFO principle (Last In, First Out).
- Uncaught RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded
- The maximum call stack size ranges from 10 to 50 thousand calls
Web APIs#
- javascript 一次只能执行一条语句,但在浏览器中,可以调用 JS 并行执行多条指令(如 ajax,访问 local storage, service workers)
- alert 等指令会 block 页面
Callback queue#
- setTimeout(fn, 100);会把 fn 放入 Callback queue 中
- 入队|出队:the callback queue follows the FIFO order (First In, First Out)
- 当 call stack 为空时,会将 callback queue 中的 task 移入 call stack 中执行
Event loop#
- JavaScript code is being run in a run-to-completion manner, meaning that if the call stack is currently executing some code, the event loop is blocked and won't add any calls from the queue until the stack is empty again
- not to block the call stack by running computation-intensive tasks.
Job queue and asynchronous code#
- 优先级高于 Callback queue | The job queue, also known as the promise queue, has priority over the callback queue,
- FIFO order(废话,这就是 queue)
- await 表达式会暂停整个 async 函数的执行进程并出让其控制权,只有当其等待的基于 promise 的异步操作被兑现或被拒绝之后才会恢复进程
- async 函数一定会返回一个 promise 对象
- 在 await 表达式之后的代码可以被认为是存在在链式调用的 then 回调中
async function async1() {
console.log("a"); // 2 - 同步执行
await async2(); // await 暂停 async1 异步执行,让出控制权,执行 async2
console.log("b"); // 6
// 等价于:
// return Promise.resolve(async2).then(() => console.log("b"));
}
async function async2() {
console.log("c"); // 3
// 等价于:
// return Promise.resolve(console.log("c"));
}
console.log("d"); // 1
setTimeout(function () {
console.log("e"); // 8
}, 0);
async1();
new Promise(function (resolve) {
console.log("f"); // 4
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log("g"); // 7
});
console.log("h"); // 5
Best Practices#
function loadImage(src){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
const img = new Image();
img.onload = () => resolve(img);
img.onerror = reject;
img.src = src;
})
}
loadImage(src)
.then(image => resizeImage(image))
.then(image> applyGrayscaleFilter(image))
.then(image => addWatermark(image))